|
BACKGROUND
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is the abrupt loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. SCA is usually caused by an electrical disturbance in the heart, which disrupts heart pumping and consequently the blood flow. In the case of a defect in electrical impulses or in the sinus node, SCA can lead to abnormal heart rhythm or arrhythmia. If not treated immediately, SCA can lead to Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD), which is the second largest cause of life-years lost in the US. Some SCD disorders are difficult to diagnose, including Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
ARVC is an inherited disease of the desmosomal proteins that hold together cardiomyocytes, and can result in sudden cardiac death. The prevalence of ARVC is as high as 1 in 1,000 individuals, accounting for 11% of SCD in adults, 22% in athletes, and 25% in children. Currently, ARVC is diagnosed using a combination of imaging and electrocardiography in addition to genetic screening. However, 2/3 of ARVC patients are gene-elusive and go undiagnosed. Disease management includes exercise restriction and an implantable defibrillator for high-risk cases.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The Hamilton lab has discovered an anti-desmosome autoantibody that is present in the blood of subjects with ARVC but is absent in healthy individuals. As an alternative to current diagnostic methods, a clinical ELISA has been developed as a simple, cost-effective test to identify the presence and severity of the ARVC condition, allowing for sensitive and specific diagnosis to inform treatment and prevent SCD.
COMMERCIAL APPLICATIONS & ADVANTAGES
Currently, ARVC diagnosis involves genetic testing and clinical testing. These existing methods are unsatisfactory: genetic testing is only 33%–50% sensitive, while clinical testing costs $1,000/year and provides only 70% sensitivity with false positives. The ARVC biomarker discovered by our researchers identifies 91% of ARVC cases, with the commercial opportunity to be developed as diagnostic biomarker.
DEVELOPMENT STAGE
ELISA assay is being developed by a CRO to research use only standards, and researchers are currently collaborating with all Canadian Inherited Arrhythmia Clinics and major US and European centres.
PATENT STATUS
Patent applications filed in Canada, US, and Europe.
|
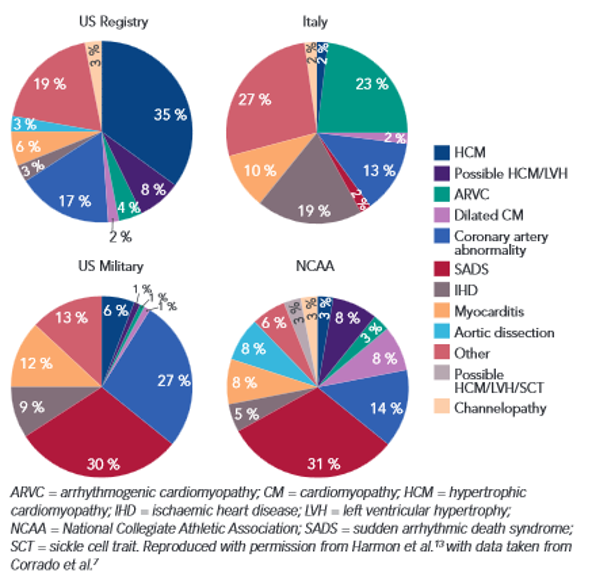 Figure 1. Comparison of causes of Sudden Cardiac Death
Figure 1. Comparison of causes of Sudden Cardiac Death
|